7 Use Cases for AI Agents in Cybersecurity
Published October 8, 2025

AI Summary
If you think your security team is strong, wait until you onboard AI agents. These aren’t just tools that add to your alert volume - they function like autonomous team members that analyze, learn, predict, and respond to threats in real time. Best of all, they make informed, non-biased decisions.
Data breach incidents rose by 70% from 2021 to 2024 - proof that cyber threats are evolving faster than defenses can keep up. Security teams are under pressure to be thorough, but with thousands of alerts flooding in daily, distinguishing real threats from background noise is a constant struggle.
While rule-based systems weren’t built for this scale or speed, learning-based AI agents offer a new path forward. They are bridging the gap between human oversight and machine autonomy to manage threats more intelligently and efficiently.
What Are AI Agents in Security?
AI agents are autonomous systems that spot, analyze, and respond to security threats without the need for constant human oversight. They operate differently from traditional AI models, like LLMs, which are often confined to specific tasks with rigid rules. In contrast, agentic AI is built to act.
These agents perceive telemetry, reason through decision models, execute tasks through their connected systems, and learn from the outcome. They operate in a feedback loop that continuously improves detection accuracy, response efficiency, and resilience against emerging attack patterns.
In cybersecurity, adaptability is a critical asset. AI can detect threats in real time, automate triage workflows, predict vulnerabilities, and contain breaches without direct supervision. Many agents can address threats across frameworks like the STRIDE threat model, spotting spoofing attempts, privilege escalation, or suspicious data access patterns as they unfold.
Some agents are reactive, others predictive, but many combine these traits to deliver continuous, adaptive protection.
Examples already in use within the industry include:
LLM-powered SOC assistants/chatbots that summarize and prioritize alerts
Autonomous pentesting agents that emulate attacker behavior to find weaknesses
Anomaly detection systems that monitor baseline behaviors and flag users, devices, and services that are acting abnormally.
5 Benefits of Using AI Agents in Modern Security Operations
Most organizations can’t afford to keep throwing more headcount and tools at their security problems. The real gap is the lack of time and focus to triage, respond, and strategize. Here are five ways AI agents can close this gap:
1. Scaling Protection
Expanding environments create more endpoints, users, and data flows to monitor, making attack surface management increasingly complex. AI agents can extend coverage automatically across systems and APIs. This elasticity makes them ideal for dynamic, fast-scaling environments where security must grow without friction.
2. Reducing Alert Fatigue
AI agents reduce the alert overload by continuously filtering and prioritizing threats based on context, severity, and behavioral patterns. Unlike static rules that trigger alerts on isolated events, AI agents look at the whole picture. They correlate data across endpoints, users, and environments to identify meaningful signals, trim alert volume, and surface relevant insights.
3. Spotting What Static Rules Miss
Attackers increasingly operate in the gray areas between known patterns. AI agents can create baselines of normal behavior, which they leverage to detect subtle shifts in login behavior or data access patterns. Signature-based detection tools would often miss these signs.
4. Decision Support
Repetitive triage and initial containment work waste your team’s expertise. Agentic AI automates routine response flows and analyzes threat intelligence, historical incident data, and contextual information to help teams make faster, evidence-based decisions. This automation frees analysts to focus on more important work.
5. Reduced MTTD and MTTR
AI agents can identify the early stages of a breach and initiate containment actions within seconds, without waiting for manual triage and incident response. This directly reduces Mean Time to Detect (MTTD) and Mean Time to Respond (MTTR), limiting attacker dwell time and the potential for escalation.
7 Use Cases for AI Agents in Cybersecurity
1. Real-Time Threat Detection and Triage
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) tools capture an enormous volume of telemetry across an environment. It’s unrealistic to expect human analysts to sort through thousands of alerts without completely missing a threat or catching it too late.
AI-based tools easily ingest and process thousands of events, adding context from logs, asset information, and threat intelligence. Triage agents don’t rely on signatures; they use anomaly detection and predictive analytics to find signals pointing to malicious behavior. These capabilities reduce the number of alerts analysts have to investigate directly, which means they have more bandwidth to focus on the meaningful threats.
2. Automated Incident Response
Once a threat is confirmed, agents can act immediately to contain the threat’s impact if armed with predefined playbooks. These playbooks define allowable actions for specific scenarios, like revoking session tokens or turning off an IAM role. Platforms like Cortex XSOAR can put these responses into practice by linking threat detections to automated agent actions through prebuilt playbooks.
The best automated response workflows clearly state full versus partial automation conditions and when to escalate for human review. To begin incorporating agentic AI for incident response, start with low-impact workflows like tagging or notifications and then progressively expand into more sensitive actions as you gain confidence in the system.
3. Anomaly and Behavior Analysis
Cyber attacks increasingly use subtle, staged behaviors (like minor privilege escalation attempts spread over time) to bypass static rule sets. AI-powered anomaly detection and behavior analysis are better equipped to notice these attacks because they establish baselines for user activity, application behavior, and endpoint traffic.
When unusual access patterns or off-hours data transfers crop up, these agents can flag them for investigation. Catching these anomalies early helps stop data exfiltration and lateral movement before they can snowball. To get the most accurate baseline, continuously feed your AI agent high-quality event data to learn and refine its understanding of what's normal in your environment.
4. Zero-Day Vulnerability Identification
Tools like Code Intelligence and GitHub CodeQL use AI to scan codebases, open-source dependencies, and runtime behaviors to detect vulnerabilities that may not yet have formal CVEs assigned. They use predictive modeling based on the catalogs of known vulnerability characteristics to recognize similar risks. For example, in 2023, the CodeQL team identified a previously unknown vulnerability in Gradle thanks to AI modeling. Developers can switch to a safer version or a different tool while investigating the potential vulnerability.
5. AI-Powered Code Security Scanning
Traditional code scanning tools can flag known vulnerabilities and common syntax-level issues, but might miss deeper vulnerabilities tied to application behavior and code logic. AI-powered security scanning can identify more complex risks like inconsistent authorization checks (which might allow privilege escalation with specific request sequences) because it can model context and intent.
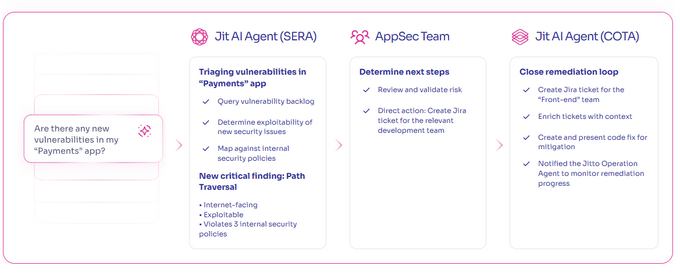
Jit is a developer-first Product Security platform that provides both robust AI-powered scanning and immediate operational value through remediation code. The platform’s Sera agent looks at runtime signals to assess whether a vulnerability is exploitable in context.
If an issue is exploitable, Jit’s Cota agent automatically creates remediation code that can quickly be applied. It also issues Jira tickets that clarify the root cause and potential business impact. These tickets support AI explainability (XAI), helping developers understand what triggered the issue and how to avoid similar patterns in the future.
Publishing technical breakdowns, secure development best practices, and remediation workflows builds trust with your audience and enhances your cybersecurity SEO. Search engines favor high-quality, authoritative content, and platforms that document and explain their approach to software security can stand out
6. Phishing and Social Engineering Detection
Email attacks are common because they have some of the lowest barriers to entry, requiring very little technical know-how. Attackers already use AI to create more effective phishing and social engineering campaigns, like targeted impersonation emails.
You can fight fire with fire by using Agentic AI countermeasures. Agents can recognize signs of a successful phish, such as unexpected OAuth grants or abnormal browser fingerprints, even when the initial message gets past filters.
For example, Abnormal creates behavioral baselines for users and vendors to quickly detect and alert your organization if an email account is compromised. For Microsoft 365 users, this tool can even force a password reset and end all active sessions.
7. Continuous Compliance Monitoring
Rather than waiting for scheduled audits, AI agents continuously monitor your compliance with standards like SOC 2, OWASP ASVS, and CIS Benchmarks. Agents can study and understand the intent behind requirements and then map those expectations to application behavior. They can then find violations in real-time, like missing audit logs or overly permissive access flows.
Jit’s AppSec and Compliance agents do just this, creating compliance finding reports and recurring tickets until the violations are resolved. The result is a faster, more continuous compliance feedback loop, reducing audit-time surprises and allowing teams to address issues before they escalate into reportable violations.
Bringing Agentic AI Into Everyday Security Workflows
Agentic AI reduces response times, filters noise, and learns in a way that traditional tools can’t. Agents can autonomously make decisions based on real-time context and changing conditions. They aren’t going to replace your security team, but they will buy back valuable time and focus that teams need to stay ahead of real threats.
Jit brings AI agents into everyday security workflows, embedding continuous security scanning, triage, and compliance directly into developer environments. It integrates intelligent, contextually relevant security into every code commit, pull request, and deployment. Surfacing only exploitable risks and automating remediation, Jit helps teams move faster while staying secure and audit-ready.
Ready to bring security and compliance up to speed with how you build software? Learn more here.